
| Student |
Teacher |
Extensions |
 |
|||
| Lesson: Bus Problem | |||
|
Setting the Stage
Doing the activity 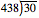  Students will usually discard the strange
looking number (.068 etc.) and use the answer with a
whole part (14.6). Long
division done the usual way yields:
_____ ____ 30 )
438 = 14 R 18 or 30 ) 438 = 14.6
which
are also popular answers to this problem. Again,
sense making is not taken into consideration when
students answer 14 R 18 or 14.6 buses. To
help students understand and learn more deeply the
the division algorithm an activity like The
Lineup: Who doesn't Belong and Why would
help.
__ Suggested lineup: 4 ÷ 16, 1/4, 4.0, .25 and 16 ) 4 Debrief A good solution for students still struggling with problem solving with division is to answer this question in a sensible and more understandable way like the solution below (Figure 2). 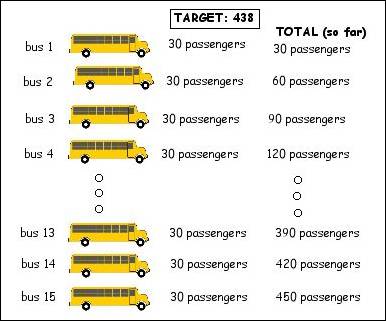 Figure 2 The student would see more clearly why 15 buses (not 14.6) are needed. Of course, this process is not as efficient as knowing what to do with the quotient after dividing, but it's a meaningful step in the right direction. |